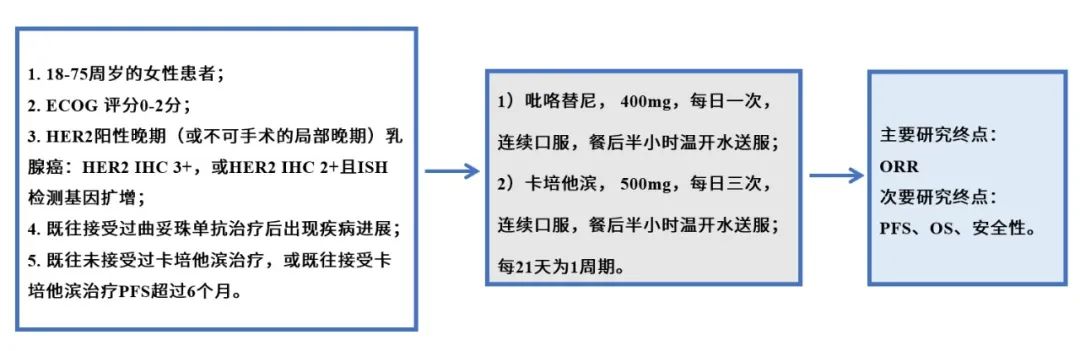
既往研究发现,褪黑素通过综合分子机制对肿瘤具有抑制作用,长链非编码核糖核酸可能参与该过程。不过,褪黑素影响三阴性乳腺癌长链非编码核糖核酸功能的具体机制尚不明确。
2021年7月16日,英国《自然》旗下《细胞死亡与疾病》在线发表中山大学肿瘤防治中心、成都中医药大学、华西大学药学院、佛山市第一人民医院的研究报告,探讨了褪黑素对三阴性乳腺癌细胞信使核糖核酸和长链非编码核糖核酸表达的影响及其相互作用机制。
该研究首先通过微阵列分析,对三阴性乳腺癌细胞4T1、891、BT549褪黑素处理前后信使核糖核酸和长链非编码核糖核酸的表达水平进行比较。随后,通过一系列体外实验和小鼠异种移植模型,分析信使核糖核酸和长链非编码核糖核酸候选物的功能及其潜在机制。
结果发现,褪黑素处理后,三阴性乳腺癌细胞的线粒体外膜蛋白FUNDC1和长链非编码核糖核酸lnc049808表达水平显著较低。利用基因技术抑制FUNDC1和lnc 049808编码基因表达水平,可抑制三阴性乳腺癌细胞的增殖、侵袭和转移。此外,lnc 049808和FUNDC1作为竞争性内源核糖核酸,主要通过结合小分子核糖核酸miR-101而抑制其促癌作用。
因此,该研究结果表明,褪黑素通过lnc 049808、FUNDC1、miR-101可抑制三阴性乳腺癌进展,有望成为三阴性乳腺癌的辅助治疗药物,故有必要进一步开展临床研究进行验证。

Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jul 16;12(8):712.
Melatonin inhibits triple-negative breast cancer progression through the Lnc049808-FUNDC1 pathway.
Yang A, Peng F, Zhu L, Li X, Ou S, Huang Z, Wu S, Peng C, Liu P, Kong Y.
Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China; Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, China; West China School of Pharmacy, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China; The First People's Hospital, Foshan, Guangdong, China.
Melatonin has been reported to have tumor-suppressive effects via comprehensive molecular mechanisms, and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) may participate in this process. However, the mechanism by which melatonin affects the function of lncRNAs in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), the most aggressive subtype of breast cancer, is still unknown. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the differentially expressed mRNAs and lncRNAs in melatonin-treated TNBC cells and the interaction mechanisms. Microarray analyses were performed to identify differentially expressed mRNAs and lncRNAs in TNBC cell lines after melatonin treatment. To explore the functions and underlying mechanisms of the mRNAs and lncRNAs candidates, a series of in vitro experiments were conducted, including CCK-8, Transwell, colony formation, lucifeRASe reporter gene, and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays, and mouse xenograft models were established. We found that after melatonin treatment, FUNDC1 and lnc049808 downregulated in TNBC cell lines. Knockdown of FUNDC1 and lnc049808 inhibited TNBC cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. Moreover, lnc049808 and FUNDC1 acted as competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) for binding to miR-101. These findings indicated that melatonin inhibited TNBC progression through the lnc049808-FUNDC1 pathway and melatonin could be used as a potential therapeutic agent for TNBC.